 |
| Important Archaeological Sites in India Map |
They moved place to place for a variety of reasons. These are:
- If they stayed at one place, they might end up all the food resources.
- In search of prey such as deer and wild cattle, they followed their movement.
- Different plants and trees bear fruits in different seasons. So they moved for different kind of fruits in every season.
- During dry season, many water sources dry up, so they move from place to place for water.
How do we know about these people?
- We came to know about hunter-gatherers by their tools and other things.
- These tools were mostly made up of either stone or wood or bones.
- Some of these tools were used to cut meat and bone, scrape bark and hides, chop fruit and roots.
- These people used wood for making handles, huts and other tools alongwith as firewood.
Choosing a place to live in
- Sites are places where the remains of things were found. These were made, used and left behind by people. These may be found on the surface of the earth, buried under the earth, or sometimes even under water.
- Most of the sites, where they lived, are close to water sources such as river and lakes.
- As stone tools were important, they also tried to find good quality stone sites.
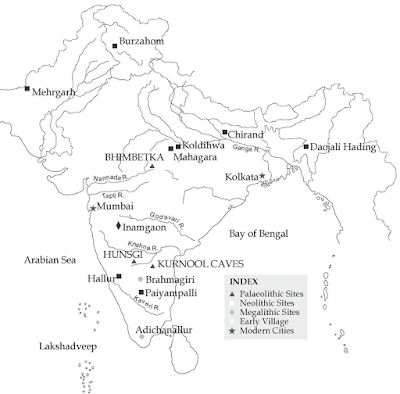
- Bhimbetka (Madhya Pradesh) and Kurnool Caves are some of the most important sites.
- These people have knowledge of fire and their paintings at Bhimbetka caves showcase their artistry.
Names and Dates
- Archaeologists have divided pre history in three ages. 1. Paleolithic Age, 2. Mesolithic Age and 3. Neolithic age.
- The Palaeolithic period extends from 2 million years ago to about 12,000 years ago. This period is again divided into the Lower, Middle and Upper Palaeolithic. It covers 99% of human history.
- The time period between 12,000 years ago and 10,000 years ago is called the Mesolithic period. In this period, tools are generally tiny and stuck on handles made up of bone and wood. These tools are known as microliths.
- From 10000 years ago onward, the age is known as Neolithic period.
A changing environment
- Around 12000 years ago, there was a major climatic phenomenon observed. The climate of earth shifted to a relatively warmer side.
- In many areas, grassland appeared from nowhere and therefore increase in grass eating animals such antelopes and so on.
- Fishing also became important during this period.
Farming and Herding
- Wheat, barley and rice naturally grew in different parts of subcontinent. Later, they were domesticated and grown on large scale.
- People also domesticated wild animal during this time.
- The wild ancestor of dog is the first animal to be domesticated. Later sheep, goat, cattle and pig were also domesticated.
Domestication
- Domestication is the process in which people grow plants and lookafter animals.
- Domestication was a gradual process that took place in many parts of the world. It began about 12,000 years ago.
- Virtually all the plant andanimal produce that we use as food today is a result of domestication.
A new way of life
- Agriculture led to various significant changes in human history. After harvesting, grains need to be stored. This led to new and big clay pottery, woven basket and pits. This also led to formation of villages and so on.
- Animals multiply naturally and provide milk and meat. They are basically reared for emergency food.
- Some of the earliest evidence of farming and herding is found in Burzahom (Kashmir), Daojali Hading (North East India), Hallur (South India) and so on.
- The earliest signs of houses found at sites like Burzahom (Kashmir). People built pit-houses, which were dug into the ground, with steps leading into them.
- Tools very different from earlier paleolithic age. They were finer, sharper and polished than their earlier variant. This is why the are called neolithic tools.
- They began weaving cloth, using different kinds of materials, such as cotton.
Mehrgarh
- It is one of the first places where people learnt to grow barley and wheat, and rear sheep and goats.
- It is located in a fertile plain, near the Bolan Pass, which is one of the most important routes into Iran.
- Most of the houses are of square or rectangular shape. Each house had four or more compartments, some are used as storage room.
- Several burial sites are found at Mehrgarh. People used to buried with material possessions and animals.
